Program Identity and Location
The design envisages a modern court building, which with its appearance clearly expresses an important public and representative function, while at the same time creating a quality public space, a new dominant in the space, and with a sustainable design, it can serve as a model for a new generation of public administration buildings.
The Design of the Building Volumes Follows the Character of the Location
The processing area is located directly next to Dunajska cesta, which is one of the city’s main veins, and also borders Topniška cesta to the north, and the park arrangement next to the existing housing buildings. The volume superimposed on the main lamella is entirely wedge-shaped, in accordance with the cities masterplan restrictions, and, like the plinth, is extended towards the stadium.
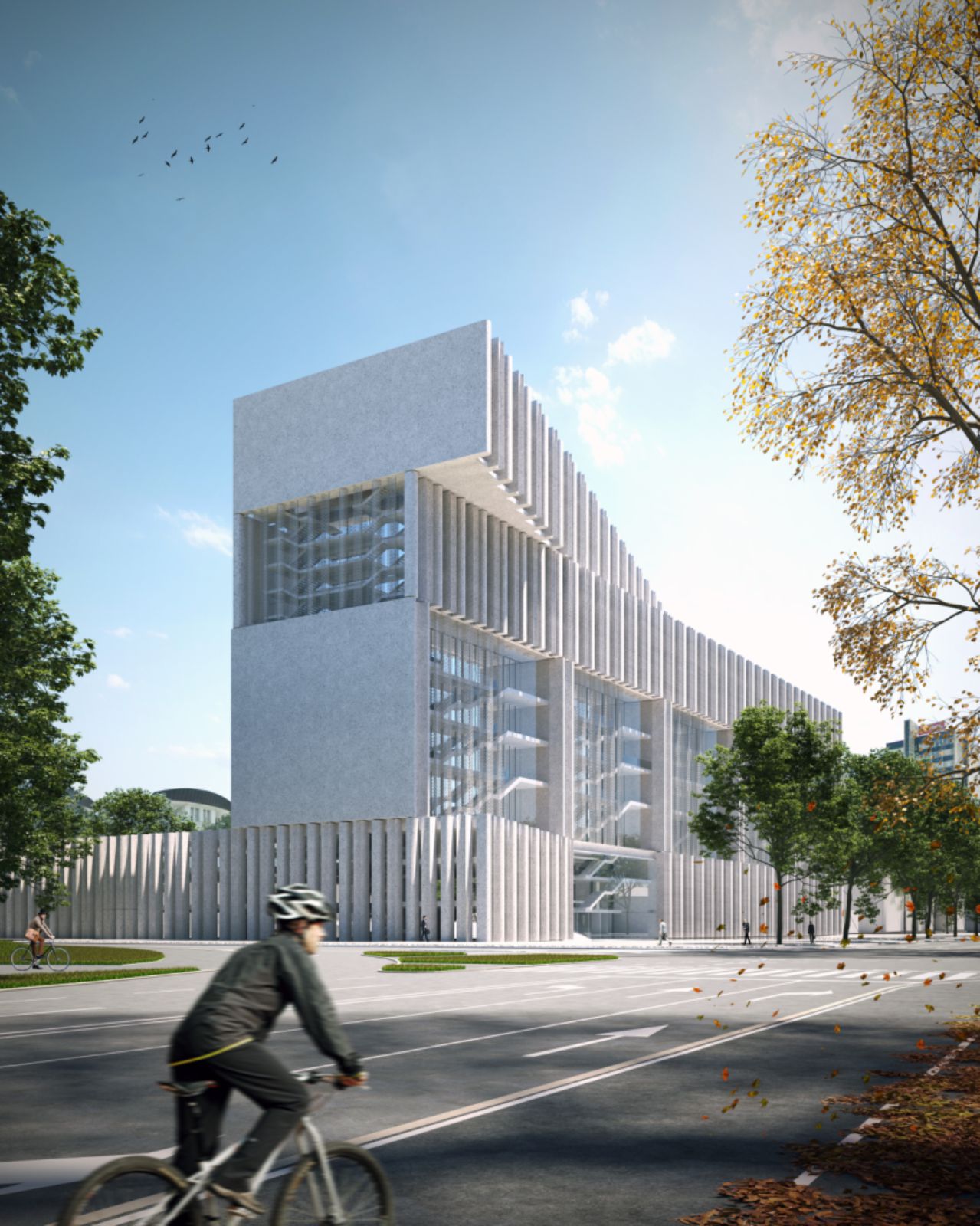

In the part of the extension, the highest volume overhangs the base lamella and establishes a compositional tension between the “floating” top of the object and its base. The entire volume is strongly defined by transversely placed vertical cores, which represent the framework into which the program in the form of courtrooms and slats with employees’ offices is inserted.
The Court as an Accessible Public Institution
The location of the building allows for good connectivity, and the position of the building establishes a wide corridor of public space along Dunajska cesta, which otherwise enables its expansion for motor traffic, but above all serves as a high-quality public area for greenery, pedestrians and cyclists. The entrance ramp for cars is located next to Topniška street, where the position is coordinated with the municipality.

The main entrance to the building offers pedestrians a quality connection between the area of the promenade along Dunajska cesta and the quieter park in the back of the building and enables entry into the building from both sides. The arrangement of the platform in the western part of the building, the areas along the Dunajska and the park in the east foresees the placement of high-quality bicycle paths and high-quality areas for pedestrians, which will encourage the use of bicycles and other sustainable forms of mobility in the area.
Structural Design
The supporting structure of the building is predominantly from reinforced concrete. The main structural system consists of six compact reinforced concrete cores made of 20 cm thick walls, which extend over the entire depth and height of the building and contain vertical communications. Despite the rugged design, the main load-bearing elements continue from the roof to the foundation and the structure is rationally designed.
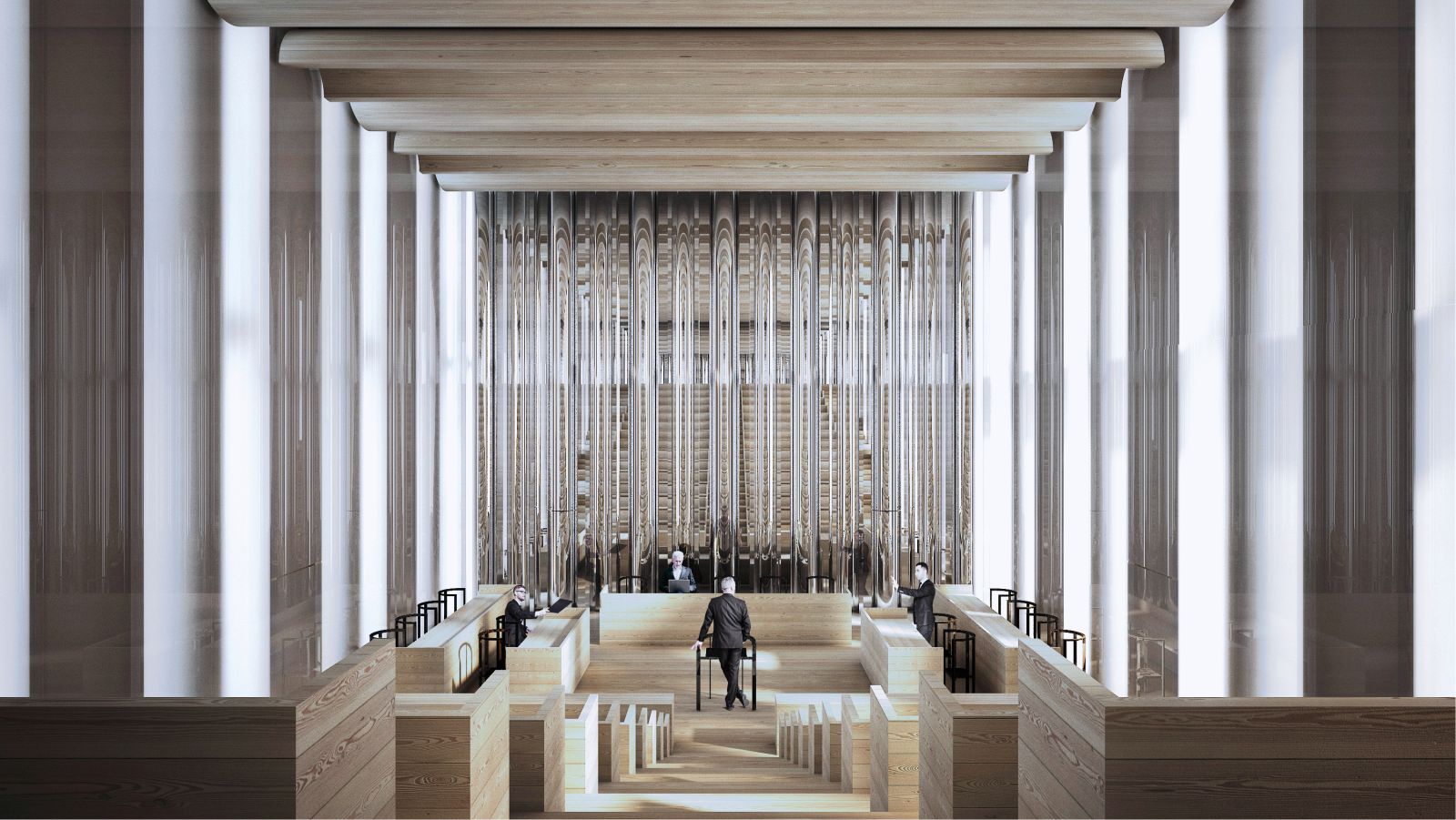

Program Design of the Facility in Relation to the Volume
The functional division of the building is designed in parallel with the volumetric design of the entire building. In the lower plinth of the building (P+2) there are publicly accessible parts of the building – the entrance with the lobby, the registrants’ rooms, information points, the premises of the investigative department of the district court, office parts of the support services for which a slightly less strict security regime is foreseen, as well as a publicly accessible restaurant and other programs intended for the public.
The upper two volumes (floors 7-9 and 10-12) are intended exclusively for employees. Four floors (floors 3-6) with a more transparent facade, where the courtrooms are located, stretch between the volumes with mainly office content, which is outwardly visible in a denser grid of facade elements and a more closed facade. The courtrooms represent the center of the court’s activities and a hub where all the actors of a particular case meet and where important decisions are made.
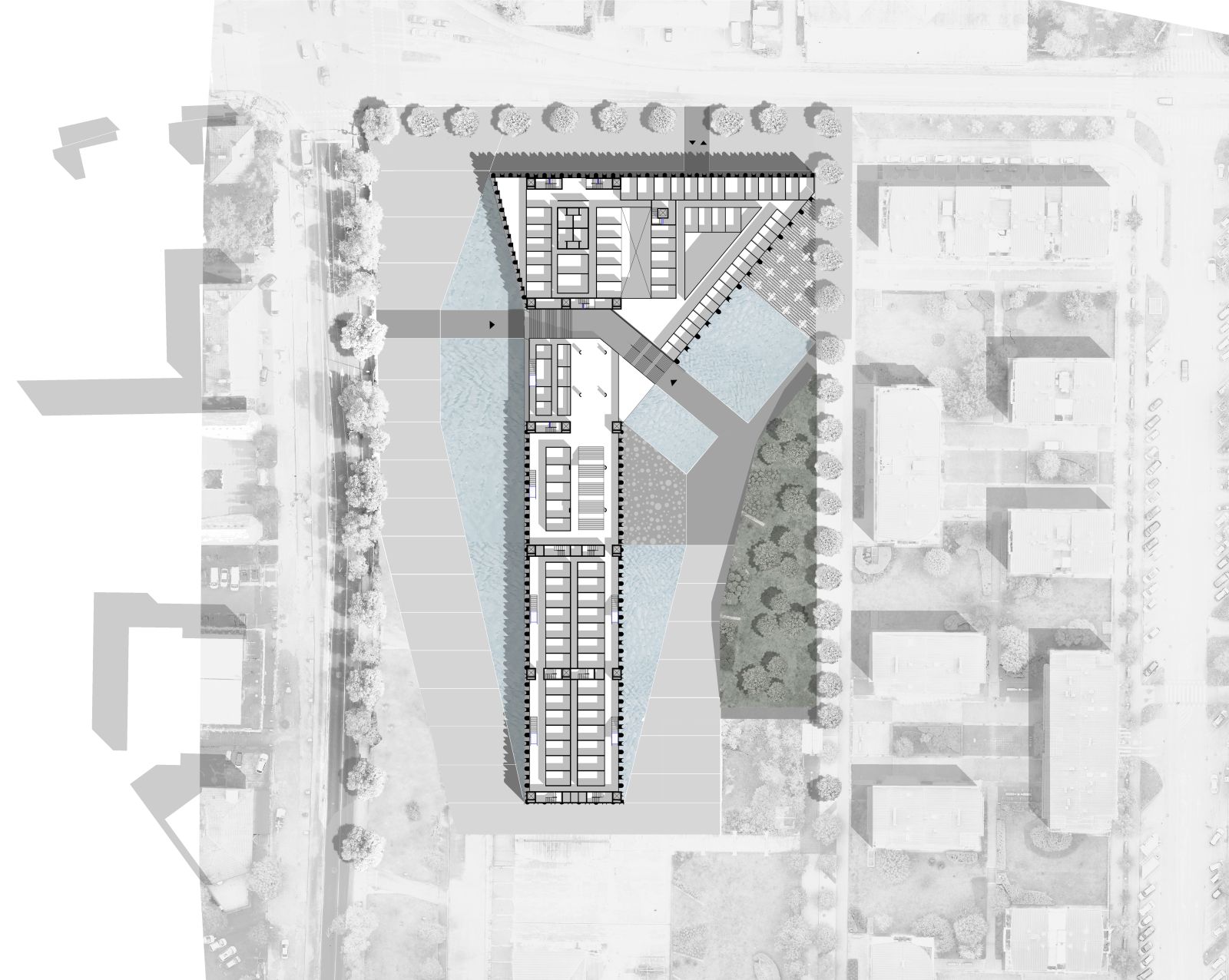

Ensuring Security while maintaining the openness of the Public Program
The functional design of the facility establishes a clear division of routes into those intended for the public, routes for employees and protected routes intended for bringing in detainees. Vertical and horizontal communications intended for the public are concentrated on the perimeter of the building as representative corridors with integrated waiting rooms and open staircases along the building, which enable indirect lighting of publicly accessible programs such as courtrooms, registration desks and the like.
Sustainable Design Through The Use Of Passive Facade Systems
The main elements of the facade are semi-circular prefabs, which in appearance soften the rigid volume of the building. They create a deep facade that directs light and shades the interior of the building. In addition, they also represent a special element for natural ventilation of interior spaces. The external shading system allows for a simultaneous reduction of cooling loads, as well as the view to the outside. Local anti-glare protection for each desk will ensure very comfortable and colorless working environments. Source and images Courtesy of ARHITEKTURA BB.

